Table of Contents
Learn the complete Initial environment examination process in Nepal with clear expert guidance to prepare and get approval for Initial Environmental Examination reports for your project.
Introduction to IEE in Nepal
The Initial Environment Examination (IEE) is a basic environmental assessment process in Nepal. It checks the possible environmental impacts of proposed projects before they start. The IEE process in Nepal in 2026 is governed by the Environment Protection Act 2076 (2019) and the Environment Protection Rules 2077 (2020), which clearly define the legal requirements and procedures for conducting an initial environmental examination in Nepal.
The main objective of an IEE is to identify and assess possible environmental impacts, both positive and negative, of a proposed project. It ensures that development activities follow environmentally sustainable practices. The initial environmental examination (IEE) process helps decision-makers and project developers clearly understand environmental impacts and take proper measures to reduce or prevent negative effects.
Legal Framework for IEE in Nepal
The legal foundation for the IEE process in Nepal is established by the following key legislation:
- Environment Protection Act 2076 (2019)
- Environment Protection Rules 2077 (2020)
- National Environmental Impact Assessment Guidelines 1993
These laws and regulations clearly define the requirements, procedures, and responsibilities of all stakeholders involved in the IEE process in Nepal. The Environment Protection Act 2076 provides the main framework for environmental protection and management in Nepal and makes environmental assessments, including the Initial environment examination nepal, mandatory for certain projects and activities.
The Environment Protection Rules 2077 explain the detailed steps and requirements for conducting IEEs. They clearly identify which projects need an IEE, the content and iee report format, and the approval procedure for an iee report Nepal. In addition, the National Environmental Impact Assessment Guidelines 1993 offer practical guidance on methods and best practices for carrying out environmental assessments in Nepal.
What Projects require an environment examination in Nepal?
In Nepal, various types of projects and activities require an IEE before implementation. The Environment Protection Rules 2077 provide a comprehensive list of projects that fall under the IEE requirement. Some examples include:
- Forest-related projects: Plantation in national forests, collection of forest products, and establishment of botanical gardens
- Industrial projects: Establishment of certain types of industries, such as dairy, vegetable oil, and processing plants
- Tourism projects: Construction of resorts, hotels, and other tourism facilities in specific areas
- Water resource and energy projects: Construction of micro-hydropower projects, rural electrification, and irrigation schemes
- Health projects: Establishment of hospitals and nursing homes with specific bed capacities
- Urban development projects: Construction of urban roads, housing developments, and solid waste management facilities
The specific thresholds and criteria for each project type are detailed in the Environment Protection Rules 2077. Project proponents must carefully review these requirements to determine if their proposed activities necessitate an IEE.
IEE Process in Nepal: Initial Environment Examination
- Step 1: Screening/Scoping of the Proposed Project
- Step 2: Preparation of the Terms of Reference
- Step 3: Approval of the Terms of Reference
- Step 4: Data Collection of Existing Environment
- Step 5: Preparation of the Final IEE Report
- Step 6: Review and Approval of the IEE Report
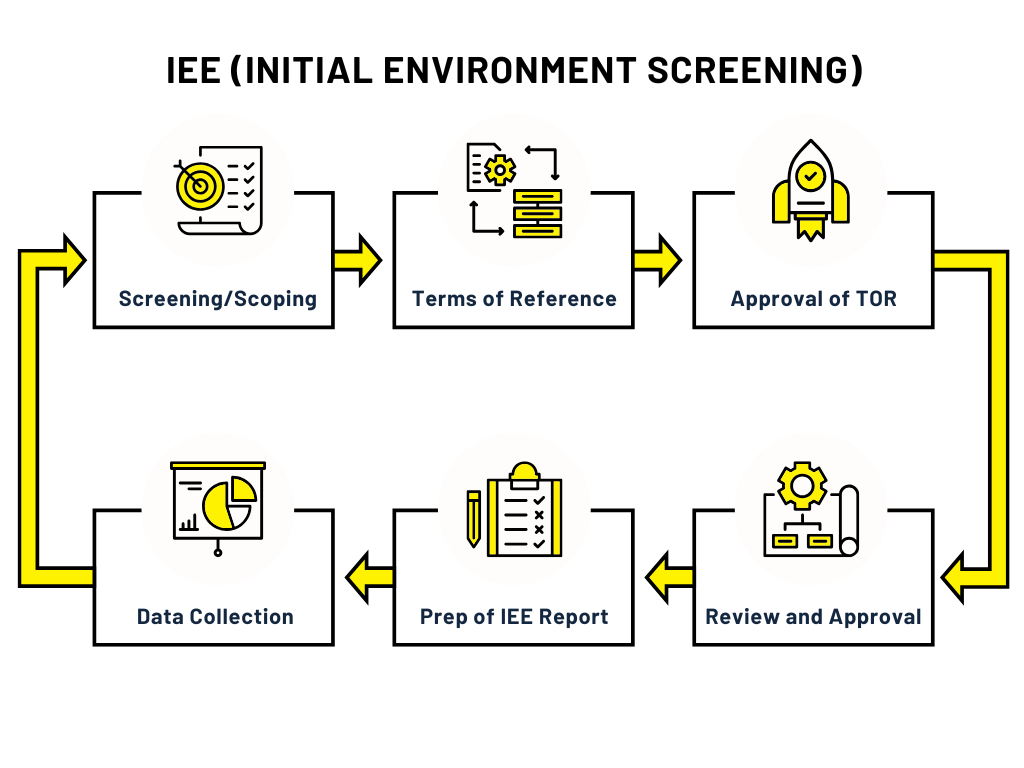
The IEE process in Nepal involves several key steps:
- Screening: Determine if the proposed project requires an IEE based on the criteria set in the Environment Protection Rules 2077.
- Scoping: Define the scope of the IEE study, including the key environmental issues to be addressed and the methodologies to be used.
- Preparation of Terms of Reference (ToR): Develop a detailed plan for conducting the IEE, including the study objectives, methodologies, and expected outcomes.
- Approval of ToR: Submit the ToR to the relevant government authority for review and approval.
- Baseline data collection: Gather information on the existing environmental conditions in the project area.
- Impact identification and analysis: Identify potential environmental impacts and assess their significance.
- Mitigation measures: Develop strategies to minimize or mitigate adverse environmental impacts.
- Public consultation: Engage with local communities and stakeholders to gather their input and concerns.
- Preparation of IEE report: Compile all findings, analyses, and recommendations into a comprehensive IEE report.
- Review and approval: Submit the IEE report to the relevant authority for review and approval.
Contents of an IEE Report
An IEE report in Nepal typically includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Description of the Proposed Project
- Description of the Existing Environment
- Identification and Analysis of Environmental Impacts
- Mitigation Measures
- Environmental Management Plan
- Public Consultation and Disclosure
- Conclusions and Recommendations
- References and Appendices
Each section provides detailed information on specific aspects of the environmental assessment. The report should be comprehensive, well-structured, and supported by relevant data and analyses.
Role of Government Agencies in IEE Process
Several government agencies play crucial roles in the IEE process in Nepal:
- Ministry of Forests and Environment: Oversees the overall environmental assessment process and provides policy guidance.
- Department of Environment: Reviews and approves IEE reports for projects under its jurisdiction.
- Sectoral ministries and departments: Review and approve IEE reports for projects within their respective sectors.
- Local governments: Participate in the review process and provide recommendations for projects within their jurisdictions.
These agencies work collaboratively to ensure that the IEE process is conducted effectively and in compliance with the relevant laws and regulations.
Public Participation in IEE Process
Public participation is an essential component of the IEE process in Nepal. The Environment Protection Rules 2077 mandate public consultation and disclosure of information during the IEE study. Key aspects of public participation include:
- Public notice: Project proponents must publish a notice in a national daily newspaper, inviting public comments on the proposed project.
- Public hearing: Organize public hearings in the project-affected areas to gather local opinions and concerns.
- Information disclosure: Make the draft IEE report available for public review and comment.
- Incorporation of public feedback: Address and incorporate relevant public comments and concerns in the final IEE report.
Effective public participation ensures that the views and concerns of local communities and stakeholders are considered in the decision-making process.
Challenges in IEE Implementation
Despite its importance, the implementation of the IEE process in Nepal faces several challenges:
- Limited technical capacity: Lack of skilled professionals to conduct comprehensive IEE studies.
- Inadequate baseline data: Insufficient environmental data for accurate impact assessment.
- Time constraints: Pressure to complete IEE studies quickly, potentially compromising quality.
- Limited public awareness: Lack of understanding among stakeholders about the IEE process and its significance.
- Weak enforcement: Inadequate monitoring and enforcement of IEE recommendations and mitigation measures.
Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from government agencies, project proponents, and environmental professionals to strengthen the IEE process in Nepal.
Benefits of Conducting IEE in Nepal
Conducting an IEE offers many benefits for project developers and the environment by supporting environmentally responsible planning through the initial environmental examination (iee) process.
- Early identification of potential environmental impacts
- Improved project design and planning
- Enhanced stakeholder engagement and public acceptance
- Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
- Reduced environmental risks and liabilities
- Promotion of sustainable development practices
- Informed decision-making by authorities and project proponents
These benefits help ensure environmentally sustainable and socially responsible project implementation through the Initial environment examination in Nepal.
Differences Between IEE and EIA in Nepal
While both IEE and Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) are environmental assessment tools, they differ in scope and complexity, which explains the difference between iee and eia.
- Scale of assessment: IEE is typically conducted for smaller projects with potentially less significant environmental impacts, while EIA is required for larger projects with potentially more significant impacts.
- Depth of analysis: IEE involves a less detailed analysis compared to EIA, which requires more comprehensive studies and data collection.
- Time and resources: IEE generally requires less time and fewer resources to complete than EIA.
- Approval process: IEE approval is often faster and involves fewer administrative steps compared to EIA.
- Public participation: While both processes involve public consultation, EIA typically requires more extensive public engagement.
Understanding these differences helps project developers choose the correct level of environmental assessment by clearly comparing eia vs iee.
Recent Developments in IEE Process
The IEE process in Nepal has undergone several recent developments:
- Digitalization: Introduction of online submission and tracking systems for IEE applications.
- Capacity building: Increased efforts to train environmental professionals and government officials in IEE methodologies.
- Sectoral guidelines: Development of sector-specific guidelines for conducting IEEs in various industries.
- Integration with SDGs: Alignment of IEE processes with Nepal’s commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Enhanced monitoring: Strengthening of post-approval monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with IEE recommendations.
These developments aim to improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and relevance of the Initial environment examination process in Nepal within Nepal’s changing environmental and development needs.
READ MORE: REGISTRATION OF SOCIAL MEDIA PLATFORM IN NEPAL
Read More
- Cost and Fees for FDI Approval in Nepal
- Cost and Fees for Foreign Branch Registration in Nepal
- Cost and Fees for Foreign Company Registration in Nepal
- Cost and Fees for Trademark Registration in Nepal
- How to Open a Commercial Bank in Nepal
- Education Consultancy Registration in Nepal
- Education consultancy License in Nepal
What is IEE in Nepal?
IEE, which stands for Initial Environmental Examination, is a basic environmental assessment used in Nepal to identify possible environmental impacts of small-scale projects. It helps evaluate how a project may affect the environment and supports authorities in deciding whether a full EIA is required. This explains the iee meaning and the iee full form in simple terms.
What are the 7 steps of EIA?
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) follows a structured process to evaluate major projects, and understanding these steps also helps clarify eia and iee in environmental assessment practices.
1. Screening
2. Scoping
3. Impact assessment
4. Mitigation measures
5. Environmental management plan
6. Public consultation
7. Reporting
How many stages are there in EIA in Nepal?
In Nepal, the EIA process generally involves four main stages, and understanding these stages also helps in comparing eia vs iee for selecting the correct environmental assessment approach.
1. Screening
2. Scoping
3. Impact analysis
4. Reporting
What is the basic EIA process?
Step 1: Determine if the project requires an EIA.
Step 2: Define key issues and impacts.
Step 3: Analyze potential environmental effects.
Step 4: Identify steps to reduce impacts.
Step 5: Track environmental performance post-implementation
Checkout out some related posts:
- https://lawaxion.com/manpower-license-process-in-nepal/
- https://taxconsultantnepal.com/nrn-citizenship-process-in-nepal-2025-2/
- https://taxconsultantnepal.com/branch-office-registration-in-nepal-contact-liaison-office/
- https://companynp.com/travel-and-tours-company-registration-in-nepal/
- https://lawaxion.com/non-resident-nepali-nrn-id-card-in-nepal/
- https://taxconsultantnepal.com/non-profit-organization-registration-process-in-nepal/
- https://lawaxion.com/education-consultancy-license-process-in-nepal/
- https://lawaxion.com/criteria-for-five-star-hotel-in-nepal/
- https://taxconsultantnepal.com/export-import-license-process-in-nepal/
- https://companynp.com/trademark-registration-process-in-nepal/
- https://taxconsultantnepal.com/company-registration-process-in-nepal/
- https://lawaxion.com/foreign-direct-investment-approval-process-in-nepal/
Professional Conclusion by Axion Partners
The Initial Environmental Examination (IEE) process in Nepal is a mandatory legal requirement to ensure development projects follow environmental laws and sustainable practices. This guide covers the complete Initial environment examination process in Nepal, including legal framework, screening, IEE report Nepal preparation, approval, and compliance. Axion Partners offers expert support to help project developers complete the IEE process in Nepal 2026 smoothly and legally.





























