Table of Contents
- 1 Step-By-Step Process of Purchasing Property
- 2 Can Foreigners Purchase Property in Nepal?
- 3 Where To Register a Foreign Company for Property Purchase in Nepal?
- 4 What Laws Govern Foreign Property Ownership in Nepal?
- 5 How To Purchase Property Through a Foreign Company in Nepal?
- 5.1 Step 1: Obtaining FDI Approval & Registering Company
- 5.2 Step 2: Injecting of Funds into the Company
- 5.3 Step 3: Conducting Due Diligence of the Property
- 5.4 Step 4: Preparation of Documents (Baina Kagaj) for Purchase
- 5.5 Step 5: Transfer of Ownership at Land Revenue Office
- 5.6 Step 6: Post-Registration Compliance and Record Maintenance
- 6 What Documents Are Required for Property Purchase?
- 7 Requirements for Purchasing Property in Nepal
- 8 How Long Does the Property Purchase Process Take?
- 9 What Are the Costs Involved in Property Purchase?
- 10 What Are Post-Registration Requirements?
- 11 What Types of Properties Can Foreign Companies Purchase?
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions
- 12.1 Can individual foreigners buy property in Nepal?
- 12.2 What is the minimum investment required for FDI company registration?
- 12.3 How to verify property ownership before purchase?
- 12.4 Can foreign companies sell property after purchase?
- 12.5 What happens if company closes after buying property?
- 12.6 Are there location restrictions for foreign property purchase?
- 12.7 What taxes apply to property ownership in Nepal?
- 12.8 Can foreign companies lease property instead of buying?
Foreigners cannot directly purchase property in Nepal under existing laws. However, foreign companies registered with Foreign Direct Investment approval can legally acquire property for business purposes. This guide explains the complete process, legal requirements, and compliance procedures.
Step-By-Step Process of Purchasing Property
- Step 1: Obtaining FDI Approval & Registering Company
- Step 2: Injecting of Funds into the Company
- Step 3: Conducting Due Diligence of the Property
- Step 4: Preparation of Documents (Baina Kagaj) for Purchase
- Step 5: Transfer of Ownership at Land Revenue Office
Can Foreigners Purchase Property in Nepal?
Foreigners cannot buy property in Nepal as individuals due to constitutional and statutory restrictions. The Constitution of Nepal and the Land Act prohibit foreign nationals from owning land or immovable property in their personal capacity. This restriction aims to protect national sovereignty and prevent speculative real estate investments by non-residents.
Foreign companies registered under the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act can acquire property for legitimate business operations. These companies must obtain prior approval from the Department of Industry and comply with sectoral regulations. The property must be used exclusively for approved business activities such as manufacturing, tourism infrastructure, or commercial operations.
The legal framework distinguishes between individual foreign ownership and corporate ownership through registered entities. Foreign Direct Investment companies enjoy property acquisition rights similar to domestic companies, provided they meet regulatory requirements. This mechanism allows foreign capital participation while maintaining control over land ownership patterns.
Where To Register a Foreign Company for Property Purchase in Nepal?
Foreign companies must register at the Department of Industry under the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies. The Department of Industry processes Foreign Direct Investment applications and issues registration certificates for eligible foreign entities. This registration serves as the legal foundation for conducting business operations and acquiring property in Nepal.
The Office of the Company Registrar handles company incorporation procedures after FDI approval. Foreign investors must submit incorporation documents, shareholder details, and business plans to the Company Registrar. The registration process establishes the legal entity authorized to hold property rights under Nepali law.
Provincial and local government offices provide additional clearances depending on the business sector and location. Certain industries require environmental clearances, municipal permits, or sectoral approvals before property acquisition. The Department of Industry coordinates with relevant authorities to facilitate the complete registration process for foreign companies seeking property ownership.
What Laws Govern Foreign Property Ownership in Nepal?
The legal framework governing foreign property ownership in Nepal includes multiple statutes and regulations:
- Constitution of Nepal 2015: Prohibits foreign nationals from owning land or immovable property in personal capacity
- Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act 2019: Permits registered foreign companies to acquire property for approved business purposes
- Land Act 1964: Restricts land ownership rights to Nepali citizens and authorized entities
- Company Act 2006: Governs incorporation and operational requirements for foreign-invested companies
- Industrial Enterprises Act 2020: Regulates industrial establishments and property acquisition for manufacturing purposes
- Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1962: Controls foreign currency transactions related to property purchases
- Land Revenue Act 1978: Establishes registration procedures and fee structures at Land Revenue Offices
- Real Estate Business Regulation Act 2016: Prohibits foreign companies from engaging in speculative real estate trading
Official Portal: Ministry of Law, Justice and Parliamentary Affairs
How To Purchase Property Through a Foreign Company in Nepal?
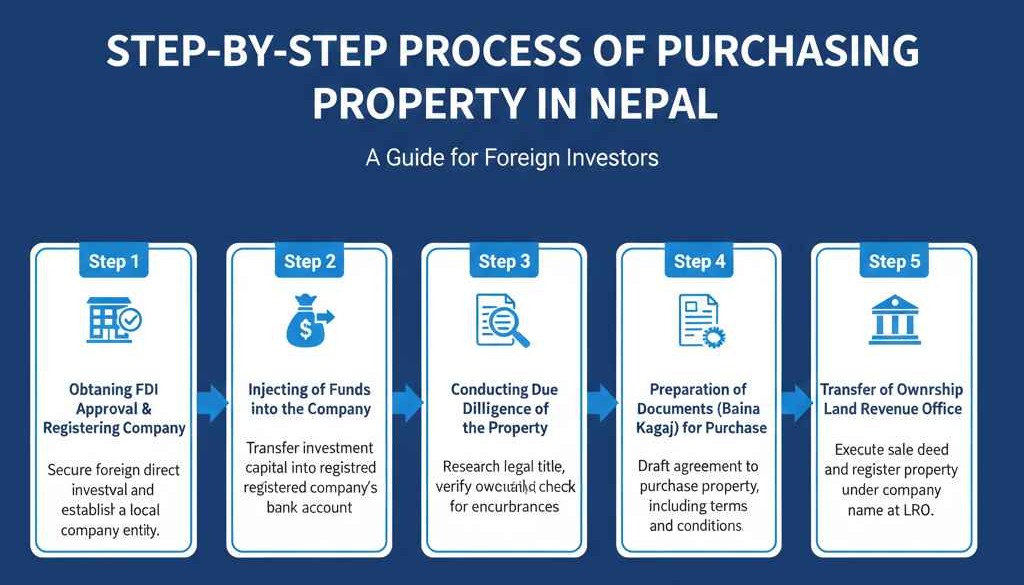
- Step 1: Obtaining FDI Approval & Registering Company
- Step 2: Injecting of Funds into the Company
- Step 3: Conducting Due Diligence of the Property
- Step 4: Preparation of Documents (Baina Kagaj) for Purchase
- Step 5: Transfer of Ownership at Land Revenue Office
- Step 6: Post-Registration Compliance and Record Maintenance
Step 1: Obtaining FDI Approval & Registering Company
Foreign investors must submit an FDI application to the Department of Industry with business plans, financial projections, and shareholder information. The application must specify the business sector, investment amount, and property requirements at Office of Company Registrar Approval typically takes thirty to forty-five days depending on application completeness and sectoral clearances.
Step 2: Injecting of Funds into the Company
Approved foreign companies must inject the committed capital through banking channels authorized by Nepal Rastra Bank. Foreign currency must be converted through licensed commercial banks with proper documentation. The company must maintain minimum capital requirements as specified in the FDI approval certificate and sectoral regulations.
Step 3: Conducting Due Diligence of the Property
Legal due diligence involves verifying property ownership records at the Land Revenue Office and confirming clear title without encumbrances. Technical due diligence assesses physical boundaries, access rights, and compliance with zoning regulations. This process typically requires fifteen working days for comprehensive verification and legal opinion preparation.
Step 4: Preparation of Documents (Baina Kagaj) for Purchase
The sale agreement document called Baina Kagaj must be prepared on official stamp paper with complete property descriptions and transaction terms. Both parties must provide citizenship certificates, company registration documents, and tax clearance certificates. Document preparation typically takes three working days with legal assistance from licensed advocates.
Step 5: Transfer of Ownership at Land Revenue Office
The buyer and seller must appear personally at the Land Revenue Office with original documents and authorized representatives. The Department of Land Management verifies documents, calculates registration fees and taxes, and records the ownership transfer. The complete transfer process takes approximately seven days from document submission to new ownership certificate issuance.
Step 6: Post-Registration Compliance and Record Maintenance
The foreign company must update property records with the Company Registrar and maintain proper accounting of the asset. Annual compliance includes property tax payments to local government and reporting to the Department of Industry. The company must ensure property usage aligns with approved business activities throughout the ownership period.
What Documents Are Required for Property Purchase?
The Documents Required for Purchasing Property as a Company are:
- Company registration certificate from Office of the Company Registrar
- Foreign Direct Investment approval certificate from Department of Industry
- Tax Registration from Inland Revenue Department
- Board resolution authorizing property purchase
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Share Registry Certificate
- Bank statements proving capital injection
- Property ownership certificate (Lalpurja) from seller
- Property valuation report from licensed valuator
- Site plan and survey documents
- Tax payment receipts for the property
- No-objection certificate from local government
- Power of attorney if representatives are signing
- Sale agreement (Baina Kagaj) on stamp paper

Requirements for Purchasing Property in Nepal
The following table outlines essential documentation requirements for foreign companies purchasing property in Nepal. Each document serves specific legal and administrative purposes in the ownership transfer process. Proper documentation ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and protects property rights.
| Document Category | Specific Documents | Issuing Authority | Validity Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company Documents | Registration Certificate, MOA, AOA | Company Registrar | Permanent |
| FDI Documents | FDI Approval Certificate | Department of Industry | Permanent |
| Tax Documents | Tax Clearance Certificate | Inland Revenue Department | 6 months |
| Property Documents | Lalpurja, Site Plan | Land Revenue Office | Current |
| Financial Documents | Bank statements, fund transfer proof | Commercial banks | 3 months |
| Authorization Documents | Board resolution, Power of Attorney | Company Board | Transaction-specific |
| Clearance Documents | NOC from Local Government | Municipal Office | 6 months |
| Valuation Documents | Property valuation report | Licensed valuer | 1 year |
How Long Does the Property Purchase Process Take?
The complete timeline for foreign companies purchasing property in Nepal varies based on regulatory approvals and documentation completeness.
The property acquisition timeline includes the following phases:
- FDI company setup and registration: Approximately thirty to forty-five days from application submission
- Capital injection and banking procedures: Seven to fifteen days depending on international transfer processing
- Property due diligence and legal verification: Fifteen working days for comprehensive title search and assessment
- Document preparation and legal drafting: Three working days with professional legal assistance
- Land Revenue Office registration and transfer: Seven days from document submission to ownership certificate issuance
- Post-registration compliance and record updates: Five to ten days for updating company records and government filings
What Are the Costs Involved in Property Purchase?
The cost structure for foreign companies purchasing property in Nepal includes government fees, professional charges, and transaction-related expenses.
| Cost Component | Amount / Percentage |
|---|---|
| Company Registration Fee | NPR 40,000 to 100,000 |
| FDI Processing Fee | As per capital amount |
| Property Brokerage Fee | 3% of transaction value |
| Land Registration Fee | 2% to 5% of property value |
| Stamp Duty | 0.5% of transaction value |
| Property Valuation Fee | NPR 20,000 to 50,000 |
What Are Post-Registration Requirements?
Foreign companies must fulfill ongoing compliance obligations after acquiring property in Nepal to maintain legal status and operational authorization.
- Annual property tax payment to local municipal or rural municipal office based on property valuation
- Submission of annual returns to the Office of the Company Registrar with updated asset schedules
- Reporting property acquisition to the Department of Industry within thirty days of registration
- Maintenance of proper accounting records showing property as company asset in financial statements
- Renewal of business licenses and operational permits as required by sectoral regulations
- Payment of corporate income tax on business profits to the Inland Revenue Department
- Compliance with land use regulations and zoning requirements of local government authorities
- Submission of annual audit reports prepared by licensed chartered accountants to regulatory authorities
- Maintenance of property insurance coverage as required by banking and regulatory requirements
- Regular updates to Nepal Rastra Bank regarding foreign investment and asset holdings
What Types of Properties Can Foreign Companies Purchase?
Foreign companies can acquire specific property types based on approved business activities and sectoral regulations. The following table categorizes permissible property acquisitions.
| Property Type | Purpose | Requirement | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Land | Manufacturing facilities and production units | Compliance with the Industrial Enterprises Act | Must be used only for approved industrial activity |
| Commercial Land | Office buildings and business operations | Municipal building permits required | Cannot be used for residential purposes |
| Tourism Property | Hotels, resorts, and tourism infrastructure | Approval from the Tourism Board | Must maintain tourism operation standards |
| Agricultural Land for Processing | Food processing and agro-based industries | Clearance from the Ministry of Agriculture | Cannot be used for speculative holding |
| Construction Land | Infrastructure development projects | Project-specific government approval | Construction must be completed within the approved timeline |
| Warehouse Property | Storage and logistics operations | Customs and trade license required | Cannot be converted to residential use |
| Real Estate Development | Not permitted for foreign companies | Prohibited under current laws | Foreign companies cannot engage in real estate trading |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can individual foreigners buy property in Nepal?
No, individual foreigners cannot buy property in Nepal under current constitutional and legal provisions. Only foreign companies registered with Foreign Direct Investment approval can acquire property for legitimate business purposes. Personal property ownership by foreign nationals remains prohibited to protect national interests.
What is the minimum investment required for FDI company registration?
The minimum investment requirement varies by sector and business type. Manufacturing industries typically require minimum investment of NPR 20 million. Service sector businesses also have the same requirement. IT Sector doesn’t require minimum investment.
How to verify property ownership before purchase?
Step 1: Obtain property identification number from seller
Step 2: Visit Land Revenue Office with property details
Step 3: Request official ownership certificate and transaction history
Step 4: Verify boundaries through site survey and inspection
Step 5: Engage legal professional for comprehensive title search
Can foreign companies sell property after purchase?
Yes, foreign companies can sell property to other eligible buyers including Nepali citizens, Nepali companies, or other registered foreign companies. The sale must follow standard property transfer procedures at the Land Revenue Office. Proceeds must be repatriated through proper banking channels.
What happens if company closes after buying property?
The company must liquidate assets including property through proper legal procedures. The liquidation process requires court approval and creditor settlement. Property must be sold to eligible buyers with proceeds distributed according to company law provisions and shareholder agreements.
Are there location restrictions for foreign property purchase?
Yes, certain areas have restrictions on foreign company property ownership. Border areas, protected zones, and strategic locations may require special permissions. Local government zoning regulations also apply. The Department of Industry provides guidance on location-specific restrictions during approval process.
What taxes apply to property ownership in Nepal?
The Applicable Taxes are:
1. Property tax paid annually to local government
2. Capital gains tax on property sale profits
3. Corporate income tax on business operations
4. Stamp duty during property registration
5. Value-added tax on construction and improvements
Can foreign companies lease property instead of buying?
Yes, foreign companies can lease property for business operations without FDI approval for property purchase. Lease agreements must be registered at local government offices. Leasing provides operational flexibility without ownership complexities. Long-term leases are common for commercial and industrial operations.




































