Table of Contents
- 1 1. What is the Statutory Procedure for FDI Approval in Nepal
- 2 2. What Is FDI in Nepal?
- 3 3. Where To Apply for FDI Approval?
- 4 4. What Are the Requirements for FDI in Nepal?
- 5 5. What Documents Are Required for FDI Approval?
- 6 6. How To Obtain FDI Approval in Nepal?
- 6.1 Step 1: Prepare Project Proposal and Obtain FCC
- 6.2 Step 2: Submit FDI Application to DOI or IBN
- 6.3 Step 3: Obtain DOI/IBN Approval and Register Company
- 6.4 Step 4: Complete Tax and Industry Registration
- 6.5 Step 5: Notify NRB and Open Bank Account
- 6.6 Step 6: Bring Investment Amount and Record at NRB
- 7 7. What Documents Must Be Submitted for FDI?
- 8 8. What are the Sector-Specific FDI Restrictions and Caps?
- 9 9. How Long Does the FDI Process Take?
- 10 10. What Are the Costs of FDI in Nepal?
- 11 11. What Are the Renewal and Compliance Requirements?
- 12 12. What Laws Govern FDI in Nepal?
- 13 13. What Types of FDI Are Permitted in Nepal?
- 14 14. What Benefits Does FDI Provide?
- 14.1 What is the minimum investment required for FDI in Nepal?
- 14.2 How long does FDI approval take?
- 14.3 When can foreign investors repatriate profits?
- 14.4 What is the FDI approval process?
- 14.5 What are FDI approval costs?
- 14.6 What documents are needed for FDI?
- 14.7 Can foreigners own 100% of Nepalese companies?
- 14.8 What taxes apply to foreign investors?
- 14.9 How is foreign investment protected?
- 14.10 What visa options exist for foreign investors?
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is the procedure of establishing company or investing in Nepal as a Foreigner. Foreign Businesses or Investors can establish companies by obtaining FDI Approval from the Department of Industry. Nepal’s FDI framework is governed by the Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2075 (2019).
The FDI process in Nepal involves obtaining regulatory approvals, meeting investment thresholds, complying with sectoral restrictions, and fulfilling post-investment obligations. Foreign investors can invest through equity participation, technology transfer, loan financing, or establishing branch operations.
The Government of Nepal has procedures through the Department of Industries and Investment Board of Nepal, offering protections including repatriation rights, national treatment, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
This guide has been prepared by Axion Partners after assisting clients from more than thirty countries in successfully making investments in Nepal. It includes the process, timelines, requirements, investment regulations, investment vehicles, and other relevant details.
1. What is the Statutory Procedure for FDI Approval in Nepal
Step 1: Verify business eligibility under positive and negative lists.
Step 2: Obtain FDI approval from Department of Industries or Investment Board of Nepal.
Step 3: Register company with Office of Company Registrar within seven days.
Step 4: Complete tax registration with Inland Revenue Department immediately after incorporation.
Step 5: Obtain industry registration certificate from Department of Industries within fifteen days.
Step 6: Bring investment amount to Nepal through banking channels within prescribed timeline.
2. What Is FDI in Nepal?
Foreign Direct Investment in Nepal refers to investment made by foreign individuals, companies, or entities in Nepalese industries and businesses. FDI is governed by the Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2075 (2019), commonly known as FITTA. This legislation replaced the earlier Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2049 (1992).
FDI in Nepal is permissible only in industrial activities, not in trading activities. The law distinguishes between sectors where foreign investment is allowed and those where it is restricted. Foreign investors must commit to invest a minimum of approximately USD 140,000 (NPR 20 million) in convertible foreign currency with the exception of IT Sector. The investment can take various forms including equity participation, technology transfer, loan financing, asset purchase, lease financing, or establishment of branch operations.
Nepal’s FDI regime operates primarily through an approval-based mechanism. Foreign investors must obtain approval from either the Department of Industries (DOI) for investments up to NPR 6 billion or the Investment Board of Nepal (IBN) for investments exceeding this threshold. The recently enacted Foreign Investment and Foreign Loan Management Bylaws, 2021 by Nepal Rastra Bank has introduced elements of automatic route, eliminating the need for central bank approval except for share purchase transactions.
3. Where To Apply for FDI Approval?
The primary approving authorities are the Department of Industries and the Investment Board of Nepal. The Department of Industries, operating under the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies, handles FDI applications for investments up to NPR 6 billion (approximately USD 51 million).
For larger investments exceeding NPR 6 billion, the Investment Board of Nepal serves as the approving authority. IBN was established to facilitate and promote large-scale foreign investment in Nepal. The board operates independently and has authority to approve mega projects across various sectors. Foreign investors can access IBN services at their office in Kathmandu. More information is available at https://www.ibn.gov.np.
Nepal Rastra Bank, the central bank of Nepal is also involved in the process. While the recent bylaws have reduced NRB’s approval requirements for most investments, approval is still mandatory for foreign investment through share purchase. All foreign investors must notify NRB before bringing investment amounts into Nepal.
4. What Are the Requirements for FDI in Nepal?
4.1. Eligibility Criteria
Foreign investors must meet several eligibility requirements to invest in Nepal. The proposed business activity must not fall under the negative list specified in FITTA. The negative list includes sectors such as small and cottage industries, personal service businesses, retail trading, real estate business (except construction), arms and ammunition manufacturing, and certain agricultural activities. The business must qualify as an industry under the Industrial Enterprises Act, 2076 (2020).
4.2. Investment Threshold Requirements
Foreign investors must invest a minimum of NPR 20 million (approximately USD 140,000) in convertible foreign currency. This threshold applies regardless of the ownership percentage held by the foreign investor. The investment amount must be brought into Nepal through proper banking channels within the prescribed timeline.
4.3. Timeline for Investment
- For investments up to NPR 50 million, 25% must be brought within one year of approval.
- For investments between NPR 50-250 million, 15% is required within one year.
- For investments between NPR 250 million to NPR 1 billion, 10% is required.
- for investments above NPR 1 billion, 5% must be brought within one year.
5. What Documents Are Required for FDI Approval?
Foreign investors must submit comprehensive documentation to obtain FDI approval from DOI or IBN. The required documents include a detailed project proposal outlining the nature of business, investment amount, business plan, and projected financial statements. If multiple investors are involved, a Joint Venture Agreement must be submitted. For individual foreign investors, biodata and notarized passport copies are required.
Corporate foreign investors must provide their certificate of incorporation, charter documents including Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association, details of direct and indirect shareholders with names, addresses, and shareholding percentages, company profile stating registered office address, business objectives, share capital, and key management personnel. Board resolution authorizing investment in Nepal, copies of directors’ passports, and latest audit reports (for investments above USD 100 million) are mandatory.
All foreign investors must obtain a Financial Credibility Certificate from their bank confirming sufficient funds for the proposed investment. If the investor cannot appear in person in Nepal, a Power of Attorney must be submitted. Additional sector-specific approvals may be required from concerned regulatory authorities. For example, telecommunications investments require approval from Nepal Telecommunications Authority, available at https://www.nta.gov.np.
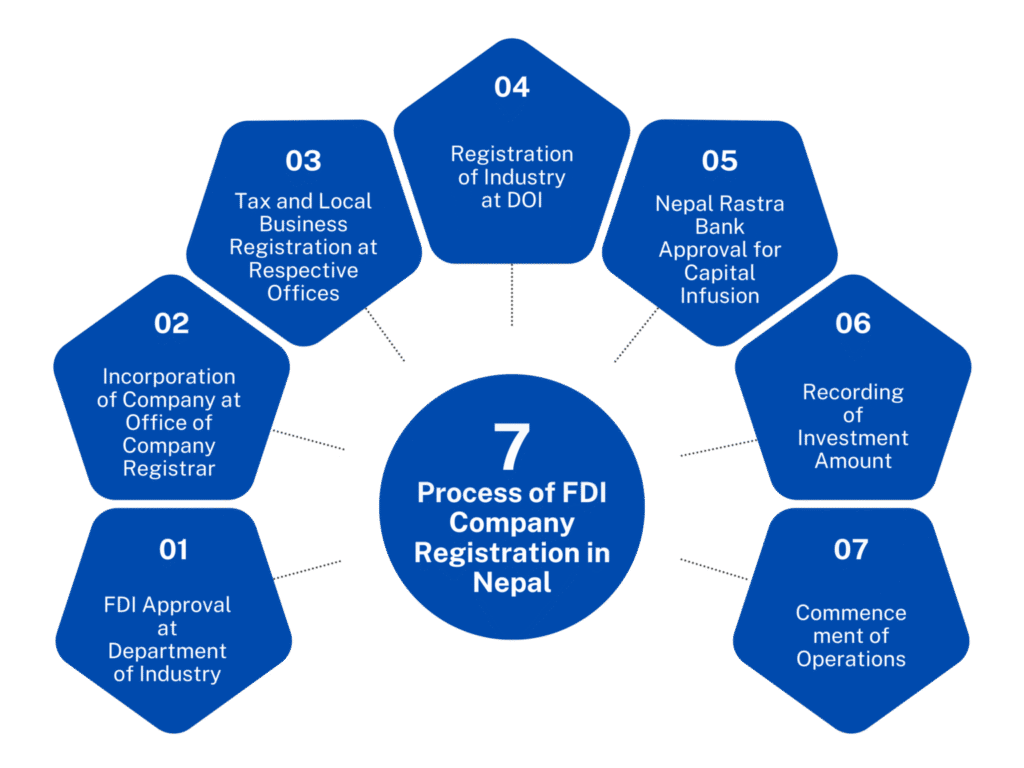
6. How To Obtain FDI Approval in Nepal?
The Process of Obtaining FDI Approval in Nepal is: Step 1: Prepare Project Proposal and Obtain FCC · Step 2: Submit FDI Application to DOI or IBN · Step 3: Obtain DOI/IBN Approval and Register Company · Step 4: Complete Tax and Industry Registration · Step 5: Notify NRB and Open Bank Account · Step 6: Bring Investment Amount and Record at NRB
Step 1: Prepare Project Proposal and Obtain FCC
Foreign investors should begin by conducting a feasibility study of the proposed business in Nepal. Prepare all required documents including project proposal, corporate documents, financial statements, and board resolutions. Ensure all foreign documents are properly notarized and translated into English if necessary. This preparatory phase typically requires seven days of careful planning and documentation gathering to ensure smooth processing of the FDI application.
Step 2: Submit FDI Application to DOI or IBN
Submit the complete FDI application with all supporting documents to the appropriate authority based on investment size. For investments up to NPR 6 billion, apply to the Department of Industries. For larger investments, submit to the Investment Board of Nepal.
The application must be submitted in the prescribed format with all required attachments. Pay applicable processing fees as determined by the regulatory authority.
The statutory timeline for approval is 15 working days from the date of complete application submission, though practical timelines may extend to 30-45 days depending on application complexity and completeness.
Step 3: Obtain DOI/IBN Approval and Register Company
Upon receiving FDI approval from DOI or IBN, proceed immediately with company registration at the Office of Company Registrar. The approval letter will specify conditions and covenants that must be fulfilled.
Register the company within 3 working days by submitting the Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association, FDI approval letter, and other required documents. The OCR will issue a company registration certificate upon successful registration.
This certificate is essential for all subsequent regulatory procedures. More information on company registration is available at https://www.ocr.gov.np.
Step 4: Complete Tax and Industry Registration
After company registration, obtain tax registration from the Inland Revenue Department. This can typically be completed within one working day through the IRD’s online portal at https://www.ird.gov.np. The Permanent Account Number (PAN) issued by IRD is mandatory for all business transactions.
Subsequently, obtain industry registration from the Department of Industries within 7 working days. Industry registration classifies the business under appropriate industrial categories and is necessary for availing tax benefits and other incentives provided under the Industrial Enterprises Act.
Step 5: Notify NRB and Open Bank Account
Before bringing investment funds into Nepal, notify Nepal Rastra Bank about the proposed foreign investment. This notification must be submitted through the prescribed format available on NRB’s website. Open a bank account with any licensed Nepalese commercial bank.
The bank will require company registration certificate, tax registration certificate, board resolution, and identification documents of authorized signatories. The bank account is necessary for receiving foreign investment funds and conducting business operations in Nepal.
Step 6: Bring Investment Amount and Record at NRB
Transfer the required percentage of investment amount from abroad to the company’s Nepalese bank account within the prescribed timeline. The bank will issue a Foreign Investment Certificate confirming receipt of foreign currency.
Within six months of receiving the investment, apply to NRB for recording the foreign investment. Submit the recording application with supporting documents including FDI approval, company registration certificate, industry registration, tax registration, foreign investment certificate from the bank, and audited financial statements.
NRB will issue a foreign investment recording certificate, which is essential for future repatriation of investment and returns.
7. What Documents Must Be Submitted for FDI?
7.1. Documents for Company Registration
- Memorandum of Association specifying company objectives and authorized capital
- Articles of Association detailing internal governance structure and procedures
- FDI approval letter from Department of Industries or Investment Board of Nepal
- Board resolution of foreign investor company authorizing investment in Nepal
- Notarized passport copies of all proposed directors and shareholders
- Proof of registered office address in Nepal through lease agreement or ownership documents
- Application form for company registration in prescribed format with applicable fees
7.2. Documents for Tax Registration
- Company registration certificate issued by Office of Company Registrar
- Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association
- Proof of registered office address with supporting documents
- Citizenship certificates or passport copies of directors and authorized representatives
- Board resolution appointing tax representative and authorizing tax registration
- Application form for Permanent Account Number in prescribed format
7.3. Documents for Industry Registration
- Company registration certificate from Office of Company Registrar
- FDI approval letter from Department of Industries or Investment Board of Nepal
- Tax registration certificate with Permanent Account Number from Inland Revenue Department
- Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association
- Proof of land ownership or lease agreement for business premises
- Environmental Impact Assessment report if required for the specific industry
- Application form for industry registration with applicable processing fees
8. What are the Sector-Specific FDI Restrictions and Caps?
| Sector | Maximum FDI Allowed | Minimum FDI Required | Regulatory Authority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banks and Financial Institutions | 85% | 20% | Nepal Rastra Bank |
| Insurance Companies | 80% | Not specified | Insurance Board |
| Telecommunication Services | 80% | Not specified | Nepal Telecommunications Authority |
| Broadcasting Media | 25% | Not specified | Ministry of Communications |
| Domestic Airlines | 49% | Not specified | Civil Aviation Authority |
| International Airlines | 80% | Not specified | Civil Aviation Authority |
| Flying Schools | 95% | Not specified | Civil Aviation Authority |
| Aircraft Maintenance | 95% | Not specified | Civil Aviation Authority |
| Consultancy Services | 51% | Not specified | Department of Industries |
| Manufacturing Industries | 100% | Not specified | Department of Industries |
| Hydropower Projects | 100% | Not specified | Department of Electricity Development |
| Tourism Industries | 100% | Not specified | Department of Tourism |
| Information Technology | 100% | Not specified | Department of Industries |
Nepal has established sector-specific investment caps to balance foreign investment benefits with domestic industry protection. The banking and financial sector allows foreign investment between 20% and 85%, ensuring significant foreign participation while maintaining domestic control. Insurance companies can have up to 80% foreign ownership, promoting international expertise in the growing insurance market.
Telecommunication services permit 80% foreign investment, recognizing the capital-intensive nature of the sector. Broadcasting media is more restrictive at 25% to preserve national cultural identity and information sovereignty. Aviation sector caps vary by activity, with domestic airlines limited to 49% foreign ownership for national security reasons, while international airlines, flying schools, and maintenance facilities allow higher percentages.
Most manufacturing, hydropower, tourism, and information technology sectors permit 100% foreign ownership, reflecting Nepal’s priority to attract maximum investment in these growth areas. Consultancy services are capped at 51% to develop local expertise. These restrictions are subject to change through government policy, and investors should verify current regulations with the Department of Industries at https://www.doi.gov.np.
9. How Long Does the FDI Process Take?
9.1. Timeline for FDI Approval
The statutory timeline for obtaining FDI approval from the Department of Industries or Investment Board of Nepal is 15 working days from the date of complete application submission. However, practical timelines often extend to 30-45 days depending on application complexity, completeness of documentation, and workload of the regulatory authority. Applications requiring additional sector-specific approvals may take longer.
9.2. Timeline for Investment Injection
Foreign investors must bring the investment amount into Nepal within prescribed timelines based on investment size. For investments up to NPR 50 million, 25% must be injected within one year of approval. For investments between NPR 50-250 million, 15% is required within one year. For investments between NPR 250 million to NPR 1 billion, 10% must be brought within one year. For investments exceeding NPR 1 billion, 5% is required within one year.
Regardless of the above percentages, 70% of total investment must be brought before the commercial operation date of the business. The remaining 30% must be injected within two years after commercial operation. These timelines can be extended by the regulatory authority upon showing reasonable cause. Failure to meet investment timelines may result in cancellation of FDI approval.
9.3. Timeline for Post-Investment Procedures
Company registration at the Office of Company Registrar typically takes 7 working days. Tax registration with the Inland Revenue Department can be completed within 1 working day through online systems. Industry registration from the Department of Industries requires approximately 15 working days. Recording of foreign investment at Nepal Rastra Bank must be completed within 6 months of investment injection and typically takes 15 working days for processing.
10. What Are the Costs of FDI in Nepal?
10.1. Government Fees and Charges
| Procedure | Fee Amount |
|---|---|
| FDI Approval (DOI) | N/A |
| FDI Approval (IBN) | As determined by IBN |
| Company Registration | Starts from NPR 9,500 |
| Tax Registration (PAN) | N/A |
| Industry Registration | NPR 20,000 |
| NRB Investment Recording | No fee |
| Business Visa | USD 35/Month |
10.2. Professional Service Costs
Foreign investors typically engage local legal counsel, accounting firms, and business consultants to navigate the FDI process. Legal fees for FDI approval and company establishment range from USD 3,000 to USD 15,000 depending on transaction complexity. Accounting and audit services cost approximately USD 1,000 to USD 5,000 annually. Business consulting for feasibility studies and market research ranges from USD 2,000 to USD 10,000.
11. What Are the Renewal and Compliance Requirements?
Foreign investment companies must fulfill ongoing compliance obligations to maintain good standing. Annual audited financial statements must be submitted to the Office of Company Registrar within six months of fiscal year end, by mid-January. The Department of Industries requires annual progress reports within the same timeline. Tax clearance certificates must be obtained from the Inland Revenue Department within three months of fiscal year end, by mid-October, with possible extension to mid-January.
Business visas for foreign investors and their representatives require annual renewal. Applications must be submitted to the Department of Immigration with recommendation from the Department of Industries at least one month before visa expiry. Work permits for foreign employees must be renewed annually through the Department of Labor. Industry registration certificates generally do not require renewal but must be updated if there are material changes in business operations.
Companies must notify the Department of Industries within 30 days of any change in foreign shareholding, particularly changes affecting 50% or more of ownership. Changes in company directors, registered office address, or business activities must be reported to the Office of Company Registrar within prescribed timelines. Failure to meet compliance requirements may result in penalties, suspension of business operations, or cancellation of FDI approval.
12. What Laws Govern FDI in Nepal?
The legal framework for foreign direct investment in Nepal comprises several key legislations and regulations. The primary law is the Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Act, 2075 (2019), which replaced the earlier 1992 act. FITTA provides the fundamental framework for foreign investment including permissible sectors, approval procedures, investment protection, and repatriation rights. The full text is available at https://www.lawcommission.gov.np.
Supporting regulations include:
- Foreign Investment and Transfer of Technology Regulation, 2077 (2021) detailing procedural aspects
- Industrial Enterprises Act, 2076 (2020) governing industrial classification and incentives
- Companies Act, 2063 (2006) regulating company formation and governance
- Income Tax Act, 2058 (2002) establishing taxation framework
- Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 2019 (1962) controlling foreign currency transactions
- Nepal Rastra Bank Act, 2058 (2002) empowering central bank oversight
- Arbitration Act, 2055 (1999) providing dispute resolution mechanisms
- Labor Act, 2074 (2017) governing employment relationships
Sector-specific laws apply to particular industries such as the Bank and Financial Institutions Act for banking sector investments, Insurance Act for insurance companies, and Telecommunications Act for telecom investments. Nepal’s Constitution, 2072 (2015) provides fundamental rights to establish and operate industries, forming the constitutional basis for investment protection.
13. What Types of FDI Are Permitted in Nepal?
| Investment Type | Description | Approval Required | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equity Investment | Formation of new company or share subscription/purchase | DOI/IBN and NRB (for share purchase) | Most common form, allows full ownership in most sectors |
| Technology Transfer | Transfer of patents, trademarks, technical know-how | DOI/IBN | Royalty payments subject to caps, repatriable after tax |
| Loan Investment | Foreign loans to Nepalese companies | Ministry approval and NRB | Subject to debt-equity ratios and interest rate limits |
| Asset Purchase | Acquisition of assets of existing companies | DOI/IBN | Useful for acquiring operational businesses |
| Lease Financing | Lease of equipment, machinery, aircraft | DOI/IBN | Common in aviation and heavy equipment sectors |
| Branch Operations | Establishment of branch of foreign company | DOI/IBN | Limited to specific sectors, full liability of parent |
Equity investment represents the most common form of FDI in Nepal, allowing foreign investors to establish new companies or acquire shares in existing entities. This form provides flexibility in ownership structure and enables investors to participate in company management. Technology transfer agreements allow foreign entities to license intellectual property, technical expertise, and know-how to Nepalese companies in exchange for royalty payments.
Loan investment enables foreign financial institutions to provide project financing to Nepalese companies, subject to approval from the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies and Nepal Rastra Bank. Asset purchase allows investors to acquire operational businesses by purchasing their assets rather than shares. Lease financing is particularly relevant for capital-intensive sectors like aviation and construction equipment.
Branch operations permit foreign companies to establish branches in Nepal, though this option is limited to specific sectors and subjects the parent company to full liability for branch operations. Each investment type has distinct regulatory requirements, tax implications, and repatriation procedures that investors must carefully consider.
14. What Benefits Does FDI Provide?
Foreign direct investment in Nepal offers numerous benefits to investors, including access to a growing South Asian market with favorable demographics. Nepal’s strategic location between India and China provides gateway opportunities to two of the world’s largest economies. The country offers competitive labor costs with a trainable workforce, particularly in manufacturing, services, and technology sectors.
Tax incentives include:
- Income tax exemptions up to 10 years for hydropower projects with 50% rebate for subsequent 5 years
- 100% tax exemption for 10 years for industries in Special Economic Zones
- Tax rebates ranging from 10-30% for industries employing large numbers of Nepalese citizens
- 20% rebate on export income with additional 35% rebate for manufacturing exports
- Reduced corporate tax rates of 20% for manufacturing and agricultural industries
- Investment protection through bilateral investment treaties with major economies
- Guaranteed repatriation of investment, profits, and proceeds in convertible currency
- National treatment ensuring foreign investors receive treatment equal to domestic investors
- Protection against expropriation except for public purpose with fair compensation
- Access to international arbitration for dispute resolution
- Business visa and work permit facilities for investors and key personnel
- One-window policy for coordinated regulatory approvals
- Membership in WTO, BIMSTEC, and SAFTA providing trade advantages
Nepal’s improving infrastructure, political stability following the 2015 Constitution, and government commitment to attracting foreign investment create an increasingly favorable environment. The country’s abundant natural resources, particularly hydropower potential, tourism attractions, and agricultural products, offer diverse investment opportunities across multiple sectors.
What is the minimum investment required for FDI in Nepal?
Foreign investors must invest at least NPR 50 million, which equals approximately USD 430,000 at current exchange rates. This minimum threshold applies regardless of the ownership percentage held by the foreign investor in the Nepalese company.
How long does FDI approval take?
The statutory timeline is 15 working days from complete application submission. Practically, the process takes 30-45 days depending on documentation completeness and application complexity. Additional time is required for sector-specific approvals.
When can foreign investors repatriate profits?
Foreign investors can repatriate dividends after one year of investment. There is no lock-in period for dividend repatriation once the initial one-year period expires. Repatriation requires approvals from DOI/IBN and NRB.
What is the FDI approval process?
Step 1: Verify business eligibility. Step 2: Prepare required documents. Step 3: Submit application to DOI or IBN. Step 4: Obtain FDI approval within 15-45 days. Complete process requires coordination with multiple regulatory authorities.
What are FDI approval costs?
Government fees range from NPR 5,000 to NPR 100,000 depending on investment size and procedures. Professional service costs including legal and accounting fees typically range from USD 5,000 to USD 20,000 for complete establishment.
What documents are needed for FDI?
1. Project proposal and business plan. 2. Corporate documents of foreign investor. 3. Financial credibility certificate from bank. 4. Board resolution authorizing investment. Additional sector-specific documents may be required.
Can foreigners own 100% of Nepalese companies?
Yes, 100% foreign ownership is permitted in most sectors including manufacturing, hydropower, tourism, and information technology. Restrictions apply to banking (85% maximum), insurance (80%), telecommunications (80%), and broadcasting (25%).
What taxes apply to foreign investors?
Corporate income tax ranges from 20-30% depending on industry. Dividend withholding tax is 5%. Capital gains tax on share sales is 25%. VAT is 13% on goods and services. Tax treaties may reduce rates.
How is foreign investment protected?
Protection includes national treatment, guaranteed repatriation rights, protection against expropriation, bilateral investment treaties with major countries, access to international arbitration, and change in law protection for approved investments.
What visa options exist for foreign investors?
1. Non-tourist visa for feasibility studies (6 months). 2. Business visa for investors and representatives (renewable annually). 3. Resident visa for investments above USD 1 million. 4. Work permits for foreign employees.





























